LangGraph Persistence - part.02
LangGraph의 Memory store(Store 인터페이스)를 통해 thread 간에 정보를 공유하는 방법을 정리
Memory store
LangGraph에서 state schema는 그래프 실행 중 채워지는 키 집합을 정의하는 스키마이다. 앞에서 본 것처럼 checkpointer는 매 스텝의 state를 thread에 기록해서 state persistence(상태 영속화)를 가능하게 한다.
하지만 여기에는 한 가지 한계가 있다. checkpointers만으로는 thread 간에 정보를 공유할 수 없다는 점이다. 예를 들어 챗봇에서 같은 사용자와 여러 대화(thread)를 나누더라도, 사용자 선호/프로필 같은 정보를 모든 대화에서 공유하고 싶을 수 있다. 이 요구가 바로 Store 인터페이스가 필요한 이유이다.
LangGraph는 thread 내부의 상태(=checkpointer)가 아니라, thread를 넘어 공유되는 정보 저장소를 위해 Store 인터페이스를 제공한다. 대표적으로 InMemoryStore를 사용하면 사용자에 대한 정보를 thread와 무관하게 저장/조회할 수 있다.
LangGraph API를 사용할 때는 store를 직접 구현/설정하지 않아도 되는 경우가 있다. API가 저장 인프라를 뒤에서 자동으로 처리하기 때문이다.
Basic usage
먼저 LangGraph와 분리해서 Store를 단독으로 사용해보는 예시이다.
1
2
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
in_memory_store = InMemoryStore()
Namespace
Memory는 tuple로 구성된 namespace에 의해 구분된다. 예를 들어 사용자 단위로 memory를 나누고 싶다면 다음처럼 (<user_id>, "memories") 형태를 쓸 수 있다. namespace의 길이는 고정이 아니며, 반드시 사용자 중심일 필요도 없다.
1
2
user_id = "1"
namespace_for_memory = (user_id, "memories")
Put
store.put으로 namespace 안에 key-value 형태의 memory를 저장한다.
- key:
memory_id같은 고유 식별자 - value: memory 내용(딕셔너리)
1
2
3
memory_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
memory = {"food_preference" : "I like pizza"}
in_memory_store.put(namespace_for_memory, memory_id, memory)
Search
store.search로 namespace에 저장된 memory들을 조회할 수 있다. 반환 값은 list이며, 가장 최근 memory가 리스트의 마지막에 위치한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
memories = in_memory_store.search(namespace_for_memory)
memories[-1].dict()
{'value': {'food_preference': 'I like pizza'},
'key': '07e0caf4-1631-47b7-b15f-65515d4c1843',
'namespace': ['1', 'memories'],
'created_at': '2024-10-02T17:22:31.590602+00:00',
'updated_at': '2024-10-02T17:22:31.590605+00:00'}
여기서 각 memory 항목은 Python 클래스인 Item 형태이다. .dict()로 변환하면 속성을 확인할 수 있다.
value: memory 값(딕셔너리)key: namespace 내에서의 고유 키namespace: memory 타입의 namespace타입은
tuple[str, ...]이지만 JSON으로 변환될 때['1', 'memories']처럼 리스트로 직렬화될 수 있다.1
{: .prompt-tip }created_at: 생성 시각updated_at: 업데이트 시각
Semantic search
단순 조회를 넘어 store는 semantic search도 지원한다. 즉, 정확히 같은 문자열이 아니라 의미 기반 검색이 가능하다. 이를 위해 store를 embedding 모델과 함께 구성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from langchain.embeddings import init_embeddings
store = InMemoryStore(
index={
"embed": init_embeddings("openai:text-embedding-3-small"), # Embedding provider
"dims": 1536, # Embedding dimensions
"fields": ["food_preference", "$"], # Fields to embed
}
)
이제 search에 자연어 query를 주면 의미적으로 가까운 memory를 찾을 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Find memories about food preferences
# (This can be done after putting memories into the store)
memories = store.search(
namespace_for_memory,
query="What does the user like to eat?",
limit=3 # Return top 3 matches
)
또한 embedding 대상으로 삼을 필드를 제어할 수 있다. fields 설정을 바꾸거나, put에서 index 옵션을 지정한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Store with specific fields to embed
store.put(
namespace_for_memory,
str(uuid.uuid4()),
{
"food_preference": "I love Italian cuisine",
"context": "Discussing dinner plans",
},
index=["food_preference"], # Only embed "food_preferences" field
)
# Store without embedding (still retrievable, but not searchable)
store.put(
namespace_for_memory,
str(uuid.uuid4()),
{"system_info": "Last updated: 2024-01-01"},
index=False,
)
index=[...]: 지정한 필드만 임베딩한다.index=False: 임베딩을 하지 않는다(조회는 가능하지만 의미 검색은 불가능하다).
Using in LangGraph
이제 store를 LangGraph에 붙이는 흐름이다. 핵심은 다음과 같다.
- checkpointer: thread 내부 상태를 저장한다.
- store: thread 바깥에서 공유될 정보를 저장한다.
즉 둘은 역할이 다르며 서로 보완 관계이다.
Compile
아래처럼 그래프를 compile할 때 checkpointer와 store를 함께 전달한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
# We need this because we want to enable threads (conversations)
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
# ... Define the graph ...
# Compile the graph with the checkpointer and store
graph = graph.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer, store=in_memory_store)
Invoke
실행 시에는 기존처럼 thread_id를 주고, 여기에 user_id를 추가로 넣어 memory namespace를 사용자 단위로 나누는 패턴을 사용한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Invoke the graph
user_id = "1"
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1", "user_id": user_id}}
# First let's just say hi to the AI
for update in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi"}]},
config,
stream_mode="updates",
):
print(update)
Node에서 store 접근
어떤 노드에서도 store: BaseStore와 config: RunnableConfig를 인자로 받으면 store 및 user_id에 접근할 수 있다.
예를 들어 대화 내용을 분석해 memory를 업데이트하는 노드는 다음과 같이 구성할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
def update_memory(state: MessagesState, config: RunnableConfig, *, store: BaseStore):
# Get the user id from the config
user_id = config["configurable"]["user_id"]
# Namespace the memory
namespace = (user_id, "memories")
# ... Analyze conversation and create a new memory
# Create a new memory ID
memory_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
# We create a new memory
store.put(namespace, memory_id, {"memory": memory})
또한 노드 내부에서 store.search로 memory를 조회한 뒤, 모델 호출에 활용할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
def call_model(state: MessagesState, config: RunnableConfig, *, store: BaseStore):
# Get the user id from the config
user_id = config["configurable"]["user_id"]
# Namespace the memory
namespace = (user_id, "memories")
# Search based on the most recent message
memories = store.search(
namespace,
query=state["messages"][-1].content,
limit=3,
)
info = "\n".join([d.value["memory"] for d in memories])
# ... Use memories in the model call
이때 memory는 list of Item으로 반환되며, 필요하면 memories[-1].dict()처럼 딕셔너리 형태로 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
memories[-1].dict()
{'value': {'food_preference': 'I like pizza'},
'key': '07e0caf4-1631-47b7-b15f-65515d4c1843',
'namespace': ['1', 'memories'],
'created_at': '2024-10-02T17:22:31.590602+00:00',
'updated_at': '2024-10-02T17:22:31.590605+00:00'}
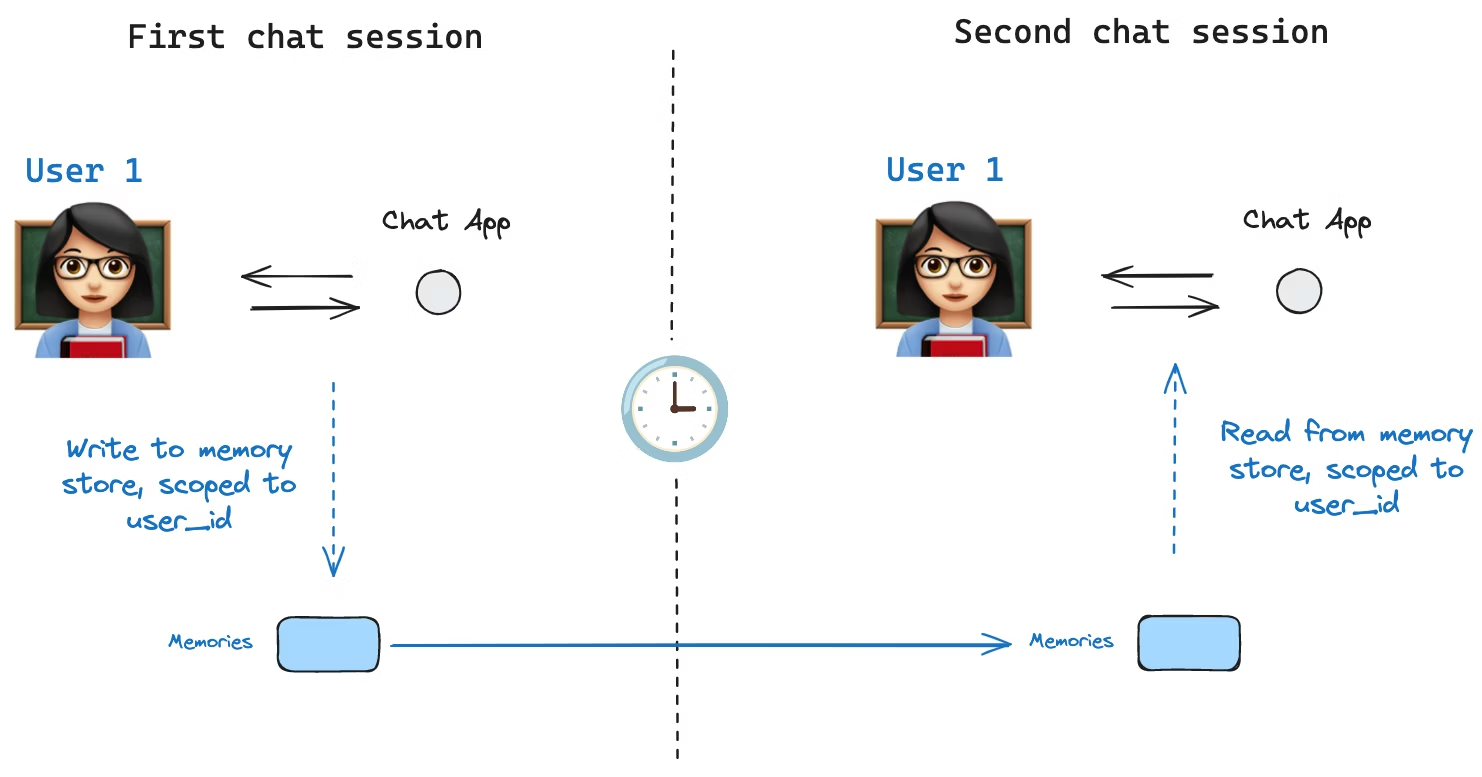
Thread를 바꿔도 memory는 유지된다
새 thread를 만들더라도 user_id가 같으면 같은 namespace를 사용하므로 memory를 계속 참조할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# Invoke the graph
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "2", "user_id": "1"}}
# Let's say hi again
for update in graph.stream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hi, tell me about my memories"}]},
config,
stream_mode="updates",
):
print(update)
LangSmith에서의 기본 store와 인덱싱 설정
LangSmith를 로컬(예: Studio) 또는 호스팅 환경에서 사용할 때는 base store가 기본 제공되어, 그래프 compile 시 store를 명시적으로 지정하지 않아도 되는 경우가 있다.
다만 semantic search(embedding 기반 검색)를 활성화하려면 langgraph.json에서 store index 설정을 해야 한다. 예시는 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
...
"store": {
"index": {
"embed": "openai:text-embeddings-3-small",
"dims": 1536,
"fields": ["$"]
}
}
}
자세한 옵션 및 배포 관련 설정은 배포 가이드를 참고하면 된다.