LangGraph Workflows와 Agents - part.1
LangGraph의 workflow/agent 개념을 정리하고, LLM augmentations와 Prompt Chaining 패턴을 예제로 이해한다.
LangGraph Workflows와 Agents - part.1
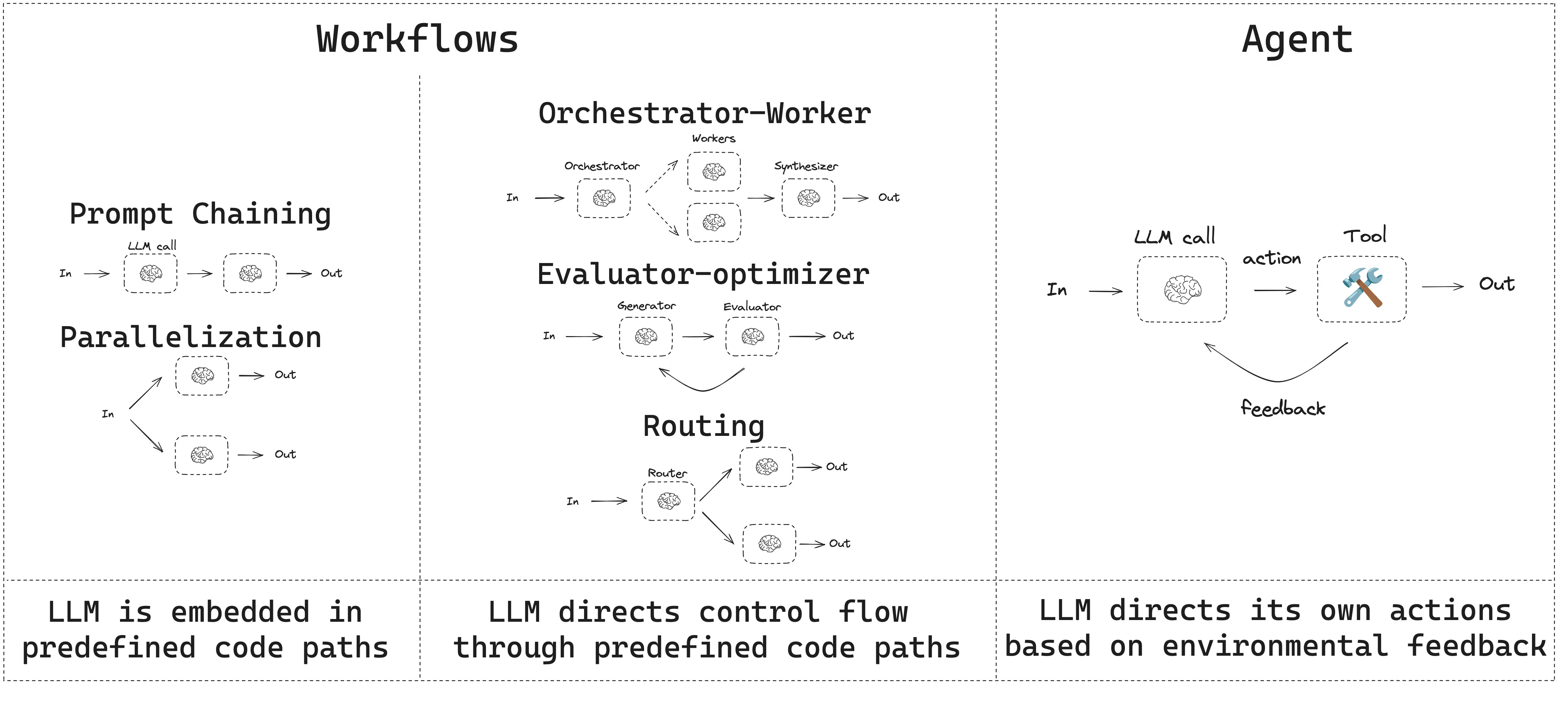
Workflows and agents
LangGraph에서 자주 등장하는 workflow 패턴과 agent 패턴 정리
- Workflows는 미리 정해진 코드 경로를 가지고 있고, 특정 순서대로 실행되도록 설계된 구조이다.
- Agents는 동적으로 동작하며, 스스로 프로세스와 툴 사용을 결정하는 구조이다.
LangGraph는 agent와 workflow를 만들 때 다음과 같은 이점을 제공한다.
- persistence
- streaming
- 디버깅 지원
- deployment 지원
Setup
workflow 또는 agent를 만들기 위해서는 structured outputs와 tool calling을 지원하는 어떤 chat model이든 사용할 수 있다. 아래 예시는 Anthropic 모델을 사용한다.
1) 의존성 설치
1
pip install langchain_core langchain-anthropic langgraph
2) LLM 초기화
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
import os
import getpass
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
def _set_env(var: str):
if not os.environ.get(var):
os.environ[var] = getpass.getpass(f"{var}: ")
_set_env("ANTHROPIC_API_KEY")
llm = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929")
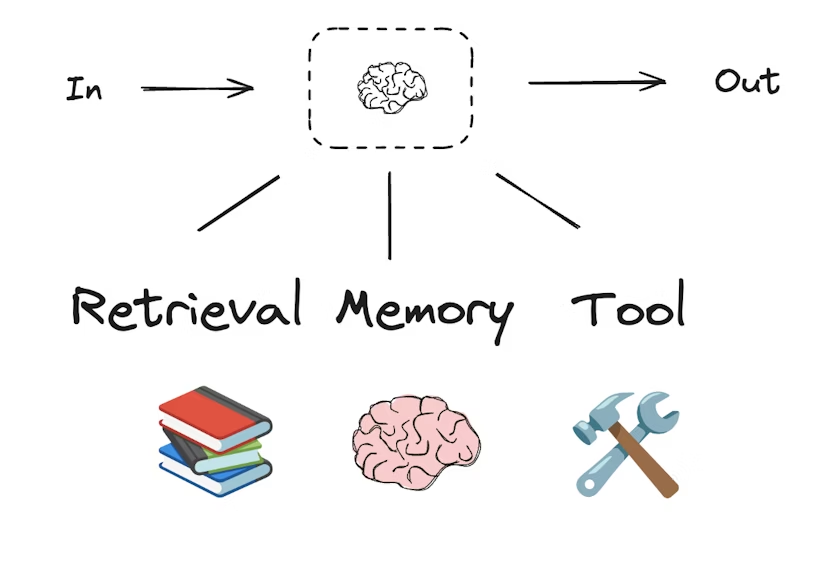
LLMs and augmentations
workflow/agentic system은 LLM과, 그 위에 덧붙이는 augmentations(확장 기능)으로 구성된다. 대표적인 augmentation은 다음과 같다.
- tool calling
- structured outputs
- short term memory
아래 코드는 structured output과 tool calling을 간단히 보여주는 예시이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# Schema for structured output
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class SearchQuery(BaseModel):
search_query: str = Field(None, description="Query that is optimized web search.")
justification: str = Field(
None, description="Why this query is relevant to the user's request."
)
# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(SearchQuery)
# Invoke the augmented LLM
output = structured_llm.invoke("How does Calcium CT score relate to high cholesterol?")
# Define a tool
def multiply(a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a * b
# Augment the LLM with tools
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools([multiply])
# Invoke the LLM with input that triggers the tool call
msg = llm_with_tools.invoke("What is 2 times 3?")
# Get the tool call
msg.tool_calls
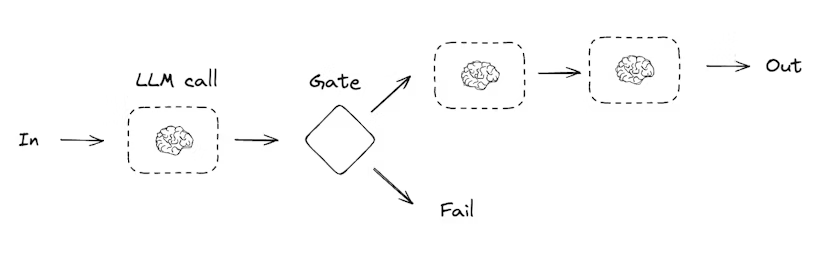
Prompt chaining
Prompt chaining은 이전 LLM 호출의 출력이 다음 LLM 호출의 입력으로 이어지는 패턴이다. 잘 정의된 작업을 더 작은 단계로 쪼개고, 각 단계를 검증 가능하게 만들 때 자주 사용된다.
대표적인 사용 예시는 다음과 같다.
- 문서를 다른 언어로 번역하기
- 생성된 결과를 일관성 관점에서 검증하기
아래는 LangGraph로 prompt chaining을 구성하는 예시이다. Graph API와 Functional API 두 방식이 함께 제시된다.
Graph API 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from IPython.display import Image, display
# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):
topic: str
joke: str
improved_joke: str
final_joke: str
# Nodes
def generate_joke(state: State):
"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a short joke about {state['topic']}")
return {"joke": msg.content}
def check_punchline(state: State):
"""Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline"""
# Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!"
if "?" in state["joke"] or "!" in state["joke"]:
return "Pass"
return "Fail"
def improve_joke(state: State):
"""Second LLM call to improve the joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: {state['joke']}")
return {"improved_joke": msg.content}
def polish_joke(state: State):
"""Third LLM call for final polish"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Add a surprising twist to this joke: {state['improved_joke']}")
return {"final_joke": msg.content}
# Build workflow
workflow = StateGraph(State)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("generate_joke", generate_joke)
workflow.add_node("improve_joke", improve_joke)
workflow.add_node("polish_joke", polish_joke)
# Add edges to connect nodes
workflow.add_edge(START, "generate_joke")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate_joke", check_punchline, {"Fail": "improve_joke", "Pass": END}
)
workflow.add_edge("improve_joke", "polish_joke")
workflow.add_edge("polish_joke", END)
# Compile
chain = workflow.compile()
# Show workflow
display(Image(chain.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
# Invoke
state = chain.invoke({"topic": "cats"})
print("Initial joke:")
print(state["joke"])
print("\n--- --- ---\n")
if "improved_joke" in state:
print("Improved joke:")
print(state["improved_joke"])
print("\n--- --- ---\n")
print("Final joke:")
print(state["final_joke"])
else:
print("Final joke:")
print(state["joke"])
Functional API 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
from langgraph.func import entrypoint, task
# Tasks
@task
def generate_joke(topic: str):
"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a short joke about {topic}")
return msg.content
def check_punchline(joke: str):
"""Gate function to check if the joke has a punchline"""
# Simple check - does the joke contain "?" or "!"
if "?" in joke or "!" in joke:
return "Fail"
return "Pass"
@task
def improve_joke(joke: str):
"""Second LLM call to improve the joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Make this joke funnier by adding wordplay: {joke}")
return msg.content
@task
def polish_joke(joke: str):
"""Third LLM call for final polish"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Add a surprising twist to this joke: {joke}")
return msg.content
@entrypoint()
def prompt_chaining_workflow(topic: str):
original_joke = generate_joke(topic).result()
if check_punchline(original_joke) == "Pass":
return original_joke
improved_joke = improve_joke(original_joke).result()
return polish_joke(improved_joke).result()
# Invoke
for step in prompt_chaining_workflow.stream("cats", stream_mode="updates"):
print(step)
print("\n")
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.