LangGraph Workflows와 Agents - part.2
LangGraph에서 Parallelization(병렬 처리)와 Routing(라우팅) 패턴을 정리하고 Graph API/Functional API 예제로 이해한다.
LangGraph Workflows와 Agents - part.2
Parallelization
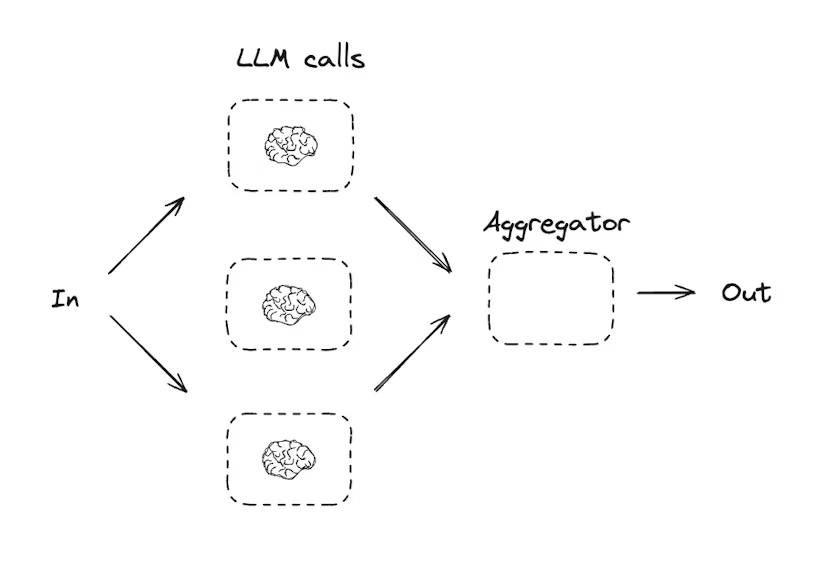
Parallelization은 여러 LLM 호출이 동시에 작업을 수행하는 패턴이다. 이는 크게 두 가지 방식으로 사용된다.
- 서로 독립적인 서브태스크를 동시에 실행한다.
- 같은 태스크를 여러 번 실행해서 서로 다른 출력들을 비교한다.
Parallelization은 보통 아래 목적에 많이 쓰인다.
- 서브태스크를 쪼개 병렬 실행해 속도를 올린다
- 같은 작업을 여러 번 실행해 결과를 비교함으로써 신뢰도를 높인다
예시는 아래와 같다.
- 한 서브태스크는 문서에서 키워드를 추출하고, 다른 서브태스크는 포맷 오류를 점검한다.
- 문서를 여러 관점으로 채점한다(예: 인용 개수, 출처 개수, 출처 품질 등).
Graph API 예시
아래 예시는 topic을 입력으로 받아, joke / story / poem을 동시에 생성한 뒤 aggregator에서 하나로 합치는 흐름이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from IPython.display import Image, display
# Graph state
class State(TypedDict):
topic: str
joke: str
story: str
poem: str
combined_output: str
# Nodes
def call_llm_1(state: State):
"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {state['topic']}")
return {"joke": msg.content}
def call_llm_2(state: State):
"""Second LLM call to generate story"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a story about {state['topic']}")
return {"story": msg.content}
def call_llm_3(state: State):
"""Third LLM call to generate poem"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a poem about {state['topic']}")
return {"poem": msg.content}
def aggregator(state: State):
"""Combine the joke, story and poem into a single output"""
combined = f"Here's a story, joke, and poem about {state['topic']}!\n\n"
combined += f"STORY:\n{state['story']}\n\n"
combined += f"JOKE:\n{state['joke']}\n\n"
combined += f"POEM:\n{state['poem']}"
return {"combined_output": combined}
# Build workflow
parallel_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Add nodes
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_1", call_llm_1)
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_2", call_llm_2)
parallel_builder.add_node("call_llm_3", call_llm_3)
parallel_builder.add_node("aggregator", aggregator)
# Add edges to connect nodes
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_1")
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_2")
parallel_builder.add_edge(START, "call_llm_3")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_1", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_2", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("call_llm_3", "aggregator")
parallel_builder.add_edge("aggregator", END)
parallel_workflow = parallel_builder.compile()
# Show workflow
display(Image(parallel_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
# Invoke
state = parallel_workflow.invoke({"topic": "cats"})
print(state["combined_output"])
Functional API 예시
Functional API에서는 @task로 병렬 실행할 작업들을 만들고, .result()로 결과를 모아 aggregator에 전달한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
from langgraph.func import entrypoint, task
@task
def call_llm_1(topic: str):
"""First LLM call to generate initial joke"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a joke about {topic}")
return msg.content
@task
def call_llm_2(topic: str):
"""Second LLM call to generate story"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a story about {topic}")
return msg.content
@task
def call_llm_3(topic):
"""Third LLM call to generate poem"""
msg = llm.invoke(f"Write a poem about {topic}")
return msg.content
@task
def aggregator(topic, joke, story, poem):
"""Combine the joke and story into a single output"""
combined = f"Here's a story, joke, and poem about {topic}!\n\n"
combined += f"STORY:\n{story}\n\n"
combined += f"JOKE:\n{joke}\n\n"
combined += f"POEM:\n{poem}"
return combined
@entrypoint()
def parallel_workflow(topic: str):
joke_fut = call_llm_1(topic)
story_fut = call_llm_2(topic)
poem_fut = call_llm_3(topic)
return aggregator(
topic, joke_fut.result(), story_fut.result(), poem_fut.result()
).result()
# Invoke
for step in parallel_workflow.stream("cats", stream_mode="updates"):
print(step)
print("\n")
Routing
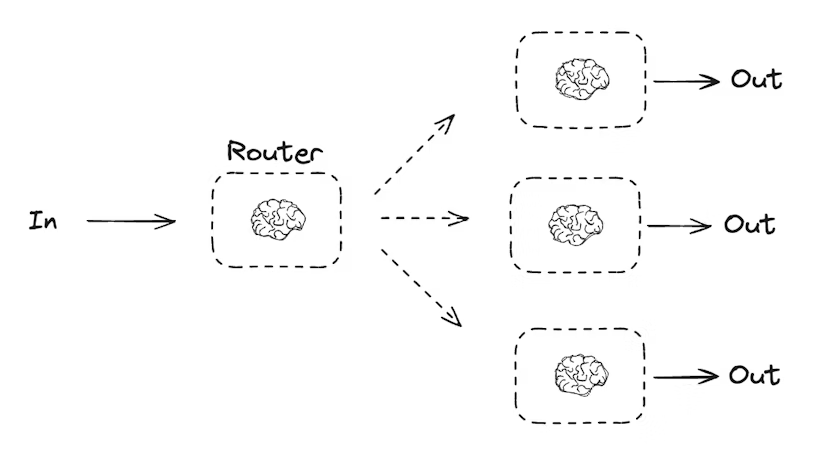
Routing 워크플로우는 입력을 먼저 처리한 다음, 상황/컨텍스트에 맞는 작업으로 분기시키는 패턴이다. 복잡한 문제에서 “전문 처리 흐름”을 미리 여러 개 만들어두고, 입력에 따라 적절한 흐름으로 보내는 식으로 사용한다.
예를 들어 “상품 관련 질문”을 처리하는 워크플로우라면, 질문 유형을 먼저 판별한 다음 아래와 같이 라우팅할 수 있다.
- 가격 문의 → pricing 프로세스
- 환불 문의 → refunds 프로세스
- 반품 문의 → returns 프로세스
Graph API 예시
아래 예시는 라우터 LLM이 입력을 보고 story / joke / poem 중 하나를 고르게 하고, 그 결정에 따라 해당 노드로 분기한다. 핵심은 다음이다.
Route스키마(Structured Output)를 라우팅 로직으로 사용한다.llm_call_router에서 decision을 만든다.add_conditional_edges()와route_decision()으로 분기한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
from typing_extensions import TypedDict, Literal
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END
from langchain.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
from IPython.display import Image, display
# Schema for structured output to use as routing logic
class Route(BaseModel):
step: Literal["poem", "story", "joke"] = Field(
None, description="The next step in the routing process"
)
# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
router = llm.with_structured_output(Route)
# State
class State(TypedDict):
input: str
decision: str
output: str
# Nodes
def llm_call_1(state: State):
"""Write a story"""
result = llm.invoke(state["input"])
return {"output": result.content}
def llm_call_2(state: State):
"""Write a joke"""
result = llm.invoke(state["input"])
return {"output": result.content}
def llm_call_3(state: State):
"""Write a poem"""
result = llm.invoke(state["input"])
return {"output": result.content}
def llm_call_router(state: State):
"""Route the input to the appropriate node"""
decision = router.invoke(
[
SystemMessage(
content="Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request."
),
HumanMessage(content=state["input"]),
]
)
return {"decision": decision.step}
# Conditional edge function to route to the appropriate node
def route_decision(state: State):
if state["decision"] == "story":
return "llm_call_1"
elif state["decision"] == "joke":
return "llm_call_2"
elif state["decision"] == "poem":
return "llm_call_3"
# Build workflow
router_builder = StateGraph(State)
# Add nodes
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_1", llm_call_1)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_2", llm_call_2)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_3", llm_call_3)
router_builder.add_node("llm_call_router", llm_call_router)
# Add edges to connect nodes
router_builder.add_edge(START, "llm_call_router")
router_builder.add_conditional_edges(
"llm_call_router",
route_decision,
{
"llm_call_1": "llm_call_1",
"llm_call_2": "llm_call_2",
"llm_call_3": "llm_call_3",
},
)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_1", END)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_2", END)
router_builder.add_edge("llm_call_3", END)
# Compile workflow
router_workflow = router_builder.compile()
# Show the workflow
display(Image(router_workflow.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))
# Invoke
state = router_workflow.invoke({"input": "Write me a joke about cats"})
print(state["output"])
Functional API 예시
Functional API에서는 llm_call_router()가 다음 스텝을 결정하고, 그 결과에 따라 실행할 task를 선택하는 방식으로 구성한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
from typing_extensions import Literal
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langgraph.func import entrypoint, task
from langchain.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
# Schema for structured output to use as routing logic
class Route(BaseModel):
step: Literal["poem", "story", "joke"] = Field(
None, description="The next step in the routing process"
)
# Augment the LLM with schema for structured output
router = llm.with_structured_output(Route)
@task
def llm_call_1(input_: str):
"""Write a story"""
result = llm.invoke(input_)
return result.content
@task
def llm_call_2(input_: str):
"""Write a joke"""
result = llm.invoke(input_)
return result.content
@task
def llm_call_3(input_: str):
"""Write a poem"""
result = llm.invoke(input_)
return result.content
def llm_call_router(input_: str):
"""Route the input to the appropriate node"""
decision = router.invoke(
[
SystemMessage(
content="Route the input to story, joke, or poem based on the user's request."
),
HumanMessage(content=input_),
]
)
return decision.step
@entrypoint()
def router_workflow(input_: str):
next_step = llm_call_router(input_)
if next_step == "story":
llm_call = llm_call_1
elif next_step == "joke":
llm_call = llm_call_2
elif next_step == "poem":
llm_call = llm_call_3
return llm_call(input_).result()
# Invoke
for step in router_workflow.stream("Write me a joke about cats", stream_mode="updates"):
print(step)
print("\n")
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.